Description
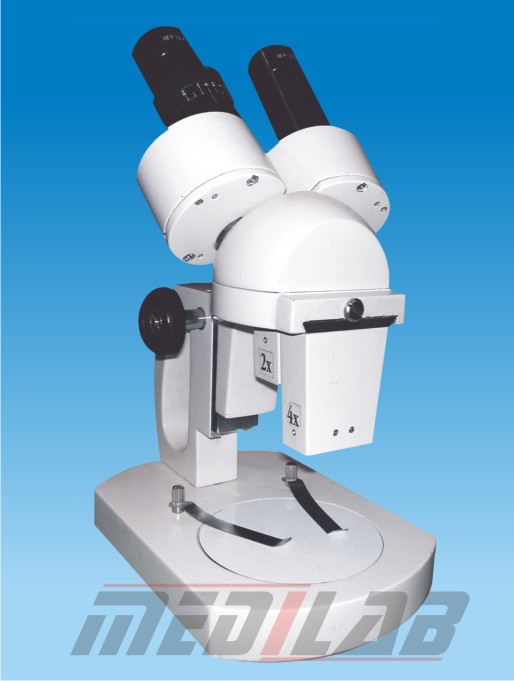
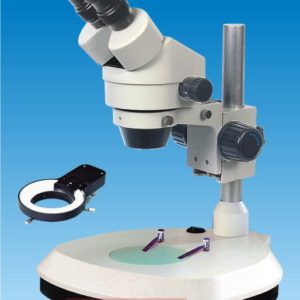
A stereo binocular microscope, also known as a dissecting microscope, is a laboratory instrument that is used for magnifying and examining three-dimensional objects at low magnifications. It is designed to provide a stereoscopic view of the specimen, which allows for better depth perception and spatial awareness.
The basic components of a stereo binocular microscope include two eyepieces that provide a binocular view, a pair of objective lenses that are positioned at a fixed distance apart, and a stage for holding the specimen. The microscope also typically includes a built-in illumination source, such as a ring light or a fiber optic light guide, to provide uniform illumination of the specimen.
Stereo binocular microscopes are commonly used in a variety of applications, including biological and medical research, industrial inspection, and materials science. They are particularly useful for examining objects with complex surface structures, such as insects, plants, or electronic components.
Stereo binocular microscopes are available in a range of designs and configurations, including models with a zoom lens for adjustable magnification and trinocular models that allow for digital imaging or photography of the specimen. They are an essential tool in many scientific fields and are valued for their ability to provide high-quality, three-dimensional imaging of small objects.