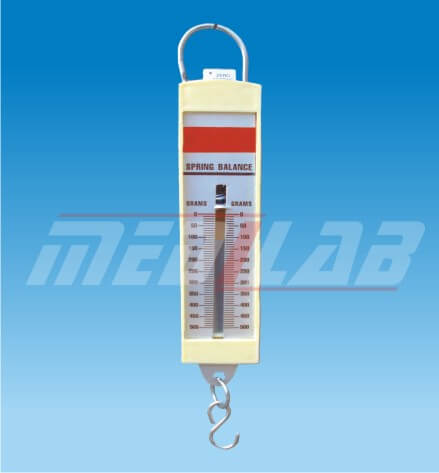
Description
A spring balance is a device used to measure force or weight using the principle of Hooke’s law. It consists of a coiled spring that is attached to a hook or loop at one end, and a pointer or digital display on the other end that shows the weight or force being applied to the spring.
When a force or weight is applied to the hook or loop, the spring stretches or compresses in proportion to the amount of force applied. This stretching or compression of the spring causes a change in its length, which is measured and displayed as the weight or force being applied.
Spring balances come in a range of sizes and weight capacities, from small handheld models that can weigh a few grams to large industrial models that can weigh several tons. They are commonly used in physics and engineering laboratories, as well as in educational settings to teach students about weight, force, and measurement.
Spring balances are easy to use and portable, making them a popular choice for outdoor activities and fieldwork where other weighing instruments may not be practical. However, they are less accurate than other types of weighing instruments such as electronic balances, and may be affected by temperature changes or other environmental factors.