Description
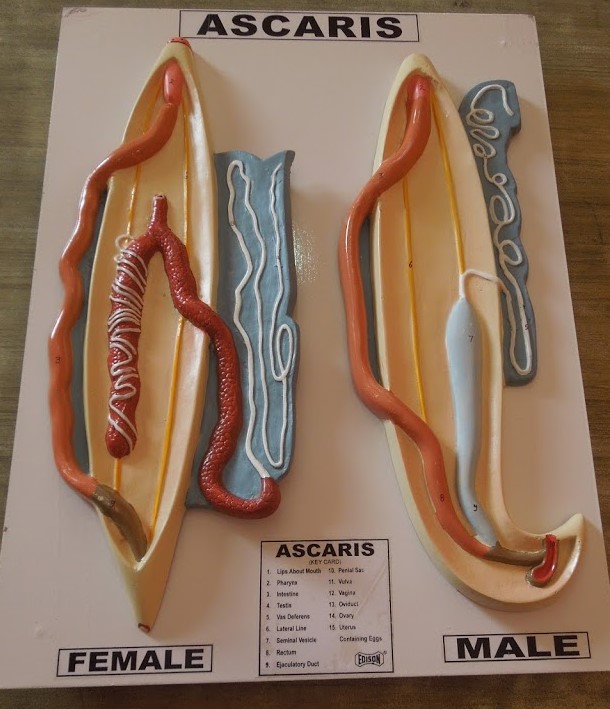
Ascaris Dissection (Male & Female) worms involves examining their reproductive systems and other anatomical features.
External anatomy
- Ascaris worms are sexually dimorphic, meaning that males and females have different body sizes, shapes, and colors.
- Male Ascaris worms are shorter and have a smaller diameter than females.
- The tail end of the male Ascaris is curved ventrally, while the tail end of the female Ascaris is pointed.
Internal anatomy
- The reproductive systems of male and female Ascaris worms are long and extended.
- The male reproductive system includes the testis, seminal vesicle, and vas deferens.
- The female reproductive system includes the ovary, oviduct, uterus, and seminal receptacle.
Dissection procedure
- To dissect an Ascaris worm, position it in a dissecting pan of water with its ventral side down.
- Rotate males slightly to accommodate the curl of their tail.
- Identify the different regions of the male and female reproductive tracts.
- Isolate tissue samples from the reproductive tracts.
- Freeze the tissue samples on dry ice and transport them to a laboratory.
Storage
- Store the tissue samples at −80 °C prior to RNA extraction.