Description
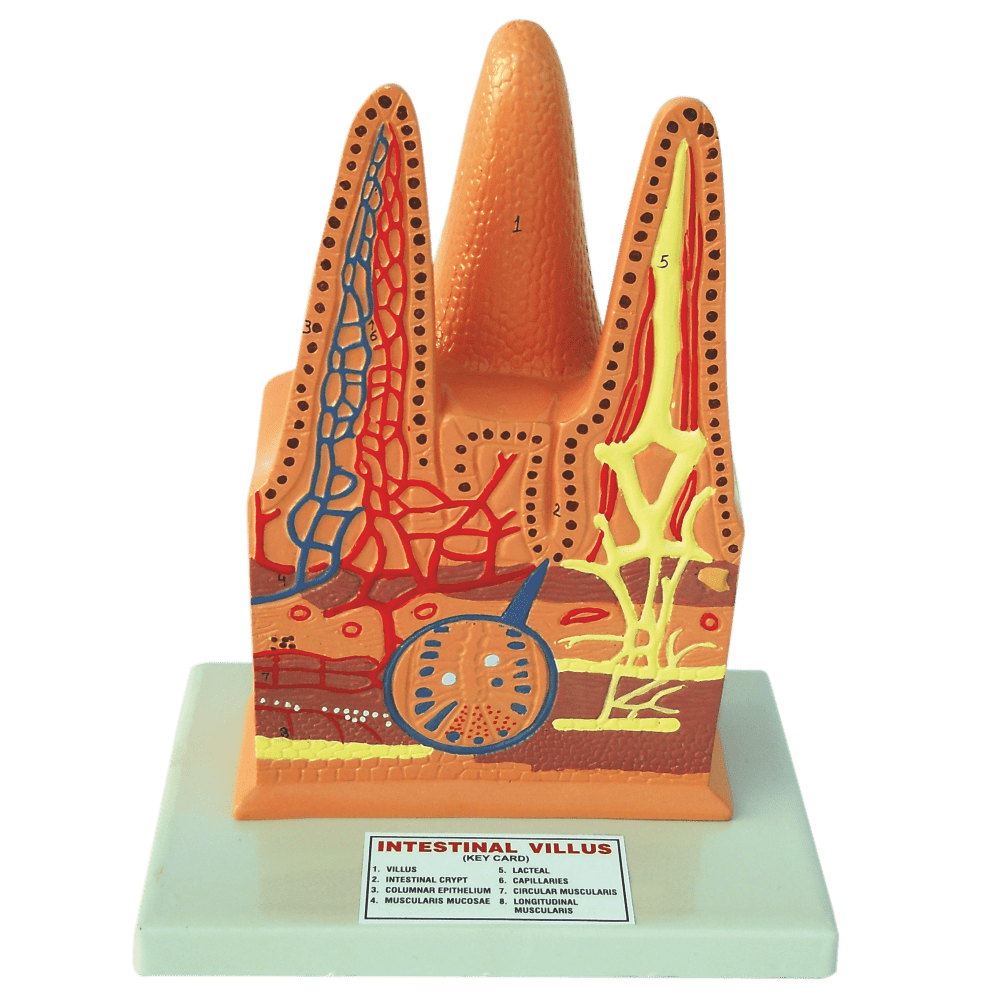
Intestinal Villus Anatomical Model are small finger-like projections in the small intestine that are important in the digestion and absorption of nutrients from the food we eat. The surface area of the intestinal villi is increased, which helps to increase the efficiency of nutrient absorption.
Each villus has a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries that transport absorbed nutrients to the rest of the body. The villi also have a network of lymphatic vessels that transport waste products and excess fluid away from the villi.
The epithelial cells that line the villi are covered in tiny microvilli, which further increase the surface area for nutrient absorption. The epithelial cells also secrete digestive enzymes that help to break down food and release nutrients.
In summary, intestinal villi are an important component of the small intestine that help to increase the efficiency of nutrient absorption and transport nutrients, waste products, and excess fluid. Understanding the anatomy and function of the intestinal villi is important in understanding the digestive process and how the body absorbs nutrients.