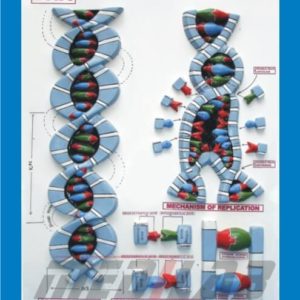
Description
Human development occurs in distinct stages, from conception to old age. Below is an overview of the major human development stages:
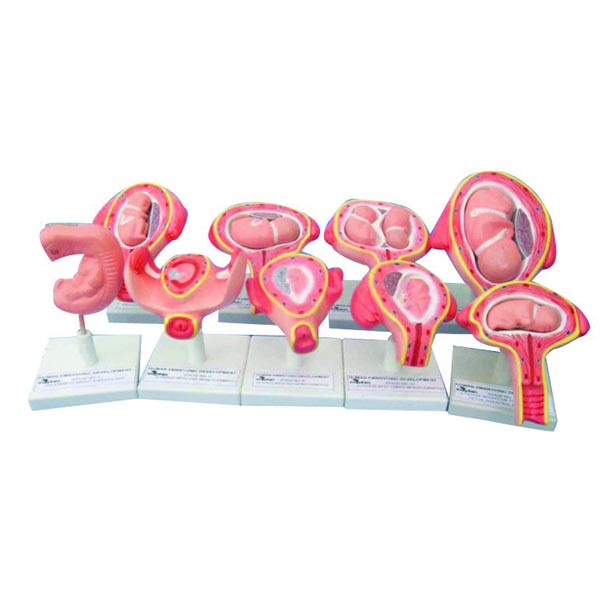
1. Prenatal Stage (Conception to Birth)
- Zygote (0-2 weeks): A fertilized egg undergoes cell division and implantation.
- Embryonic Stage (3-8 weeks): Formation of major organs and body structures.
- Fetal Stage (9 weeks-birth): Rapid growth and maturation of organs.
2. Infancy (Birth to 2 Years)
- Reflexes such as sucking and grasping develop.
- Rapid brain growth, motor skills (crawling, walking), and sensory development.
- Emotional bonding and early social interactions begin.
3. Early Childhood (2-6 Years)
- Development of language, coordination, and fine motor skills.
- Social skills and imagination expand.
- Basic independence in daily tasks like dressing and feeding.
4. Middle Childhood (6-12 Years)
- Logical thinking and problem-solving abilities develop.
- Academic learning and peer relationships become important.
- Physical growth continues steadily.
5. Adolescence (12-18 Years)
- Puberty occurs, leading to hormonal and physical changes.
- Identity formation, emotional independence, and cognitive maturity.
- Social interactions and peer influence play a significant role.
6. Early Adulthood (18-40 Years)
- Establishment of career, relationships, and independence.
- Physical peak in terms of strength and energy.
- Family and social responsibilities grow.
7. Middle Adulthood (40-65 Years)
- Gradual physical decline (metabolism slows, wrinkles, gray hair).
- Career and family stability, focus on legacy and accomplishments.
- Mid-life transitions and possible reevaluation of life goals.
8. Late Adulthood (65+ Years)
- Aging leads to reduced strength, sensory decline, and potential health issues.
- Reflection on life, wisdom, and emotional stability increase.
- Retirement and lifestyle adjustments.